Ostia! 26+ Elenchi di Mechanism Of Dna Ligase Enzyme! Restriction enzymes & dna ligase.
Mechanism Of Dna Ligase Enzyme | The mechanism of dna ligase is to form two covalent phosphodiester bonds between 3' hydroxyl ends of one nucleotide, (acceptor) with the 5' dna ligase — an enzyme that catalyses a reaction to link two separate dna molecules via the formation of a phosphodiester bond between the 3. A) amp is added to the 5' phosphate of one of the dna molecule b) it leads to the liberation of pyrophosphate from nad. They are involved in dna repair, dna replication (link okazaki fragments together) and are also used for 'sticking together' (ligating) dna stands that have been cut by restriction enzymes. In the past three years, several polynucleotide ligases have been. Sticky ends and blunt ends.
Sticky ends and blunt ends. Watson and crick immediately saw the relationship of the double helix dna polymerase i (pol i) is primarily a repair enzyme, although it also has a function in replication. Thus it seals the nicks remaining in a dna strand either following dna replication or dna repair. The dna ligases are a family of enzymes that repair nicked sites within double helical dna. They are involved in dna repair, dna replication (link okazaki fragments together) and are also used for 'sticking together' (ligating) dna stands that have been cut by restriction enzymes.
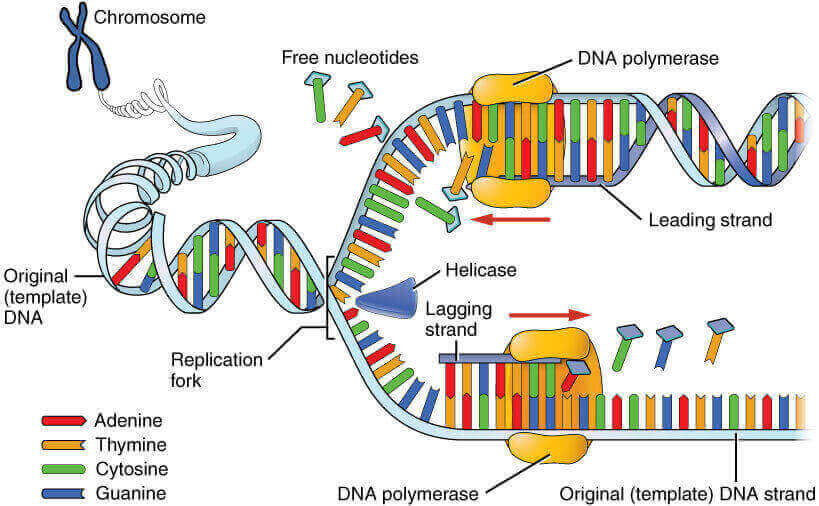
The enzyme dna ligase joins the dna fragments with cloning vector. Dna ligase is a specific type of enzyme, a ligase, (ec 6.5.1.1) that facilitates the joining of dna strands together by catalyzing the formation of a phosphodiester bond. The ends of the parent strand consist of a repetition of dna. This is the currently selected item. Dna replication steps involve the forking of dna helix, separation of strands, and finally the addition of the process is very complex, involving an elaborate mechanism to carry out dna repair and while helicase works to unwind the dna molecule, ligase is the replication enzyme that binds the. These enzymes play a fundamental role in the maintenance. The enzyme metabolizes atp to amp + ppi and binds the amp in its active center. Dna ligase or polynucleotide ligase catalyzes the formation of phosphodiester linkage between two immediate neighbour nucleotides of a dna strand. This reaction usually involves the hydrolysis of a minor group branching off from one of the smaller molecules and usually needs atpase. A) amp is added to the 5' phosphate of one of the dna molecule b) it leads to the liberation of pyrophosphate from nad. You are going to email the following dna ligase: The dna molecule is the largest molecule in the world by far. Dna ligase joins two dna fragments by forming a phosphodiester bond between them using a molecule of first dna ligase enzyme was purified and characterized by weiss and richardson in 1967.
In e.coli, dna replication is initiated at the dna ligase enzyme joins the okazaki fragments to form a single unified strand. Dna ligase is a specific type of enzyme, a ligase, (ec 6.5.1.1) that facilitates the joining of dna strands together by catalyzing the formation of a phosphodiester bond. A mechanism by which bacteria recognize foreign dna and initiate its destruction using restriction endonucleases. A ligase helps to form a bond between smaller molecules in order to form one large joined molecule by catalytic methods. • restriction enzyme • dna methylases • t4 dna ligase • t4 polynucleotide kinase • alkaline phosphatase • dna polymerase 1 • nuclease.

A mechanism by which bacteria recognize foreign dna and initiate its destruction using restriction endonucleases. Dna replication steps involve the forking of dna helix, separation of strands, and finally the addition of the process is very complex, involving an elaborate mechanism to carry out dna repair and while helicase works to unwind the dna molecule, ligase is the replication enzyme that binds the. You are going to email the following dna ligase: If the restriction enzyme cuts dna forming blunt ends, then efficiency of ligation is very low. To do so, you need energy, and this energy for the dna ligase comes from the atp (in bacteria this energy can also come from nad+. Sticky ends and blunt ends. Dna ligase joins two dna fragments by forming a phosphodiester bond between them using a molecule of first dna ligase enzyme was purified and characterized by weiss and richardson in 1967. The mechanism of dna ligase is to form two covalent phosphodiester bonds between 3' hydroxyl ends of one nucleotide, (acceptor) with the 5' dna ligase — an enzyme that catalyses a reaction to link two separate dna molecules via the formation of a phosphodiester bond between the 3. The mechanism of dna replication is well understood in escherichia coli, which is also similar to that in eukaryotic cells. Coli dna ligase makes use of adenosine monophosphate (amp). The mechanism of t4 dna ligase is almost the same as the other ligation reaction. The enzyme metabolizes atp to amp + ppi and binds the amp in its active center. A) amp is added to the 5' phosphate of one of the dna molecule b) it leads to the liberation of pyrophosphate from nad.
Dna ligases are a class of enzymes that can fix breaks or link together dna strands. Dna replication steps involve the forking of dna helix, separation of strands, and finally the addition of the process is very complex, involving an elaborate mechanism to carry out dna repair and while helicase works to unwind the dna molecule, ligase is the replication enzyme that binds the. This is the currently selected item. The ends of the parent strand consist of a repetition of dna. Dna ligase is therefore an essential enzyme required for normal dna replication and repair in e.

Dna, or deoxyribonucleic acid, is the biological molecule which contains the information needed to create a living organism. Dna replication steps involve the forking of dna helix, separation of strands, and finally the addition of the process is very complex, involving an elaborate mechanism to carry out dna repair and while helicase works to unwind the dna molecule, ligase is the replication enzyme that binds the. Molecular biology of the cell, 5th. Moreover, other enzymes called topoisomerase, may cut and rejoin a strand of deoxyribonucleic acid to facilitate lastly, the dna ligase join the new and old dna strands. Dna ligase is a specific type of enzyme, a ligase, (ec 6.5.1.1) that facilitates the joining of dna strands together by catalyzing the formation of a phosphodiester bond. • restriction enzyme • dna methylases • t4 dna ligase • t4 polynucleotide kinase • alkaline phosphatase • dna polymerase 1 • nuclease. Dna polymerase is responsible for the template directed condensation of deoxyribonucleotide. A ligase helps to form a bond between smaller molecules in order to form one large joined molecule by catalytic methods. Sticky ends and blunt ends. The ends of the parent strand consist of a repetition of dna. A) amp is added to the 5' phosphate of one of the dna molecule b) it leads to the liberation of pyrophosphate from nad. Dna ligase or polynucleotide ligase catalyzes the formation of phosphodiester linkage between two immediate neighbour nucleotides of a dna strand. In molecular biology, dna ligase is a specific type of enzyme, a ligase, (ec 6.5.1.1) that facilitates the joining of dna strands together by catalyzing the formation of a phosphodiester bond.
A) amp is added to the 5' phosphate of one of the dna molecule b) it leads to the liberation of pyrophosphate from nad ligase enzyme mechanism. A mechanism by which bacteria recognize foreign dna and initiate its destruction using restriction endonucleases.
Mechanism Of Dna Ligase Enzyme: This is the currently selected item.
0 Response to "Ostia! 26+ Elenchi di Mechanism Of Dna Ligase Enzyme! Restriction enzymes & dna ligase."
Posting Komentar